Node discovery
This tutorial demonstrates how to discover other nodes in the network and retrieve information about each node. Two applications are implemented in this tutorial:
- Passive network monitor - a small application that simply listens to messages of type
uavcan.protocol.NodeStatus, which allows it to obtain the following minimal information about each node:- Node ID
- Operating mode (Initialization, Operational, Maintenance, etc.)
- Health code (OK, Warning, Error, Critical)
- Uptime
- Active network monitor - an application that extends the passive monitor so that it actively requests
uavcan.protocol.GetNodeInfowhenever a node appears in the network or restarts. This allows the monitor to obtain the following information about each node:- All information from the passive monitor (see above)
- Node name
- Software version information
- Hardware version information, including the globally unique ID and the certificate of authenticity
Refer to the applications provided with the Linux platform drivers to see some real-world examples of network monitoring.
Passive monitor
#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <uavcan/uavcan.hpp>
#include <uavcan/protocol/node_status_monitor.hpp> // For uavcan::NodeStatusMonitor
extern uavcan::ICanDriver& getCanDriver();
extern uavcan::ISystemClock& getSystemClock();
/**
* This class implements a passive node monitor.
* There's a basic node monitor implementation in the library: uavcan::NodeStatusMonitor
* Extension through inheritance allows to add more complex logic to it.
*/
class NodeMonitor : public uavcan::NodeStatusMonitor
{
/**
* This method is not required to implement.
* It is called when a remote node becomes online, changes status, or goes offline.
*/
void handleNodeStatusChange(const NodeStatusChangeEvent& event) override
{
if (event.was_known)
{
std::cout << "Node " << int(event.node_id.get()) << " has changed status from "
<< modeToString(event.old_status) << "/" << healthToString(event.old_status)
<< " to "
<< modeToString(event.status) << "/" << healthToString(event.status)
<< std::endl;
}
else
{
std::cout << "Node " << int(event.node_id.get()) << " has just appeared with status "
<< modeToString(event.status) << "/" << healthToString(event.status)
<< std::endl;
}
}
/**
* This method is not required to implement.
* It is called for every received message uavcan.protocol.NodeStatus after handleNodeStatusChange(), even
* if the status code has not changed.
*/
void handleNodeStatusMessage(const uavcan::ReceivedDataStructure<uavcan::protocol::NodeStatus>& msg) override
{
(void)msg;
//std::cout << "Remote node status message\n" << msg << std::endl << std::endl;
}
public:
NodeMonitor(uavcan::INode& node) :
uavcan::NodeStatusMonitor(node)
{ }
static const char* modeToString(const NodeStatus status)
{
switch (status.mode)
{
case uavcan::protocol::NodeStatus::MODE_OPERATIONAL: return "OPERATIONAL";
case uavcan::protocol::NodeStatus::MODE_INITIALIZATION: return "INITIALIZATION";
case uavcan::protocol::NodeStatus::MODE_MAINTENANCE: return "MAINTENANCE";
case uavcan::protocol::NodeStatus::MODE_SOFTWARE_UPDATE: return "SOFTWARE_UPDATE";
case uavcan::protocol::NodeStatus::MODE_OFFLINE: return "OFFLINE";
default: return "???";
}
}
static const char* healthToString(const NodeStatus status)
{
switch (status.health)
{
case uavcan::protocol::NodeStatus::HEALTH_OK: return "OK";
case uavcan::protocol::NodeStatus::HEALTH_WARNING: return "WARNING";
case uavcan::protocol::NodeStatus::HEALTH_ERROR: return "ERROR";
case uavcan::protocol::NodeStatus::HEALTH_CRITICAL: return "CRITICAL";
default: return "???";
}
}
};
int main()
{
uavcan::Node<16384> node(getCanDriver(), getSystemClock());
/*
* In this example the node is configured in passive mode, i.e. without node ID.
* This means that the node will not be able to emit transfers, which is not needed anyway.
*/
node.setName("org.uavcan.tutorial.passive_monitor");
const int node_start_res = node.start();
if (node_start_res < 0)
{
throw std::runtime_error("Failed to start the node; error: " + std::to_string(node_start_res));
}
/*
* Instantiating the monitor.
* The object is noncopyable.
*/
NodeMonitor monitor(node);
/*
* Starting the monitor.
* Once started, it runs in the background and does not require any attention.
*/
const int monitor_start_res = monitor.start();
if (monitor_start_res < 0)
{
throw std::runtime_error("Failed to start the monitor; error: " + std::to_string(monitor_start_res));
}
/*
* Spinning the node for 2 seconds and then printing the list of nodes in the network.
*/
if (node.spin(uavcan::MonotonicDuration::fromMSec(2000)) < 0)
{
throw std::runtime_error("Spin failed");
}
std::cout << "Known nodes:" << std::endl;
for (int i = 1; i <= uavcan::NodeID::Max; i++)
{
if (monitor.isNodeKnown(i))
{
auto status = monitor.getNodeStatus(i);
std::cout << "Node " << i << ": "
<< NodeMonitor::modeToString(status) << "/" << NodeMonitor::healthToString(status)
<< std::endl;
/*
* It is left as an exercise for the reader to call the following services for each discovered node:
* - uavcan.protocol.GetNodeInfo - full node information (name, HW/SW version)
* - uavcan.protocol.GetTransportStats - transport layer statistics (num transfers, errors, iface stats)
* - uavcan.protocol.GetDataTypeInfo - data type check: is supported? how used? is compatible?
*/
}
}
/*
* The monitor provides a method that finds first node with worst health.
*/
if (monitor.findNodeWithWorstHealth().isUnicast())
{
/*
* There's at least one node in the network.
*/
auto status = monitor.getNodeStatus(monitor.findNodeWithWorstHealth());
std::cout << "Worst node health: " << NodeMonitor::healthToString(status) << std::endl;
}
else
{
/*
* The network is empty.
*/
std::cout << "No other nodes in the network" << std::endl;
}
/*
* Running the node.
*/
node.setModeOperational();
while (true)
{
const int res = node.spin(uavcan::MonotonicDuration::fromMSec(1000));
if (res < 0)
{
std::cerr << "Transient failure: " << res << std::endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
Active monitor
#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <uavcan/uavcan.hpp>
#include <uavcan/protocol/node_info_retriever.hpp> // For uavcan::NodeInfoRetriever
extern uavcan::ICanDriver& getCanDriver();
extern uavcan::ISystemClock& getSystemClock();
/**
* This class will be collecting information from uavcan::NodeInfoRetriever via the interface uavcan::INodeInfoListener.
* Please refer to the documentation for uavcan::NodeInfoRetriever to learn more.
*/
class NodeInfoCollector final : public uavcan::INodeInfoListener
{
struct NodeIDHash
{
std::size_t operator()(uavcan::NodeID nid) const { return nid.get(); }
};
std::unordered_map<uavcan::NodeID, uavcan::protocol::GetNodeInfo::Response, NodeIDHash> registry_;
/**
* Called when a response to GetNodeInfo request is received. This happens shortly after the node restarts or
* becomes online for the first time.
* @param node_id Node ID of the node
* @param response Node info struct
*/
void handleNodeInfoRetrieved(uavcan::NodeID node_id,
const uavcan::protocol::GetNodeInfo::Response& node_info) override
{
registry_[node_id] = node_info;
}
/**
* Called when the retriever decides that the node does not support the GetNodeInfo service.
* This method will never be called if the number of attempts is unlimited.
*/
void handleNodeInfoUnavailable(uavcan::NodeID node_id) override
{
// In this implementation we're using empty struct to indicate that the node info is missing.
registry_[node_id] = uavcan::protocol::GetNodeInfo::Response();
}
/**
* This call is routed directly from @ref NodeStatusMonitor.
* Default implementation does nothing.
* @param event Node status change event
*/
void handleNodeStatusChange(const uavcan::NodeStatusMonitor::NodeStatusChangeEvent& event) override
{
if (event.status.mode == uavcan::protocol::NodeStatus::MODE_OFFLINE)
{
registry_.erase(event.node_id);
}
}
/**
* This call is routed directly from @ref NodeStatusMonitor.
* Default implementation does nothing.
* @param msg Node status message
*/
void handleNodeStatusMessage(const uavcan::ReceivedDataStructure<uavcan::protocol::NodeStatus>& msg) override
{
auto x = registry_.find(msg.getSrcNodeID());
if (x != registry_.end())
{
x->second.status = msg;
}
}
public:
/**
* Number if known nodes in the registry.
*/
std::uint8_t getNumberOfNodes() const
{
return static_cast<std::uint8_t>(registry_.size());
}
/**
* Returns a pointer to the node info structure for the given node, if such node is known.
* If the node is not known, a null pointer will be returned.
* Note that the pointer may be invalidated afterwards, so the object MUST be copied if further use is intended.
*/
const uavcan::protocol::GetNodeInfo::Response* getNodeInfo(uavcan::NodeID node_id) const
{
auto x = registry_.find(node_id);
if (x != registry_.end())
{
return &x->second;
}
else
{
return nullptr;
}
}
};
int main(int argc, const char** argv)
{
if (argc < 2)
{
std::cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " <node-id>" << std::endl;
return 1;
}
const int self_node_id = std::stoi(argv[1]);
uavcan::Node<16384> node(getCanDriver(), getSystemClock());
node.setNodeID(self_node_id);
node.setName("org.uavcan.tutorial.active_monitor");
const int node_start_res = node.start();
if (node_start_res < 0)
{
throw std::runtime_error("Failed to start the node; error: " + std::to_string(node_start_res));
}
/*
* Initializing the node info retriever object.
*/
uavcan::NodeInfoRetriever retriever(node);
const int retriever_res = retriever.start();
if (retriever_res < 0)
{
throw std::runtime_error("Failed to start the retriever; error: " + std::to_string(retriever_res));
}
/*
* This class is defined above in this file.
*/
NodeInfoCollector collector;
/*
* Registering our collector against the retriever object.
* The retriever class may keep the pointers to listeners in the dynamic memory pool,
* therefore the operation may fail if the node runs out of memory in the pool.
*/
const int add_listener_res = retriever.addListener(&collector);
if (add_listener_res < 0)
{
throw std::runtime_error("Failed to add listener; error: " + std::to_string(add_listener_res));
}
/*
* Running the node.
* The application will be updating the list of nodes in the console window.
*/
node.setModeOperational();
while (true)
{
const int res = node.spin(uavcan::MonotonicDuration::fromMSec(500));
if (res < 0)
{
std::cerr << "Transient failure: " << res << std::endl;
}
/*
* Rendering the info to the console window.
* Note that the window must be large in order to accommodate information for multiple nodes (use smaller font).
*/
std::cout << "\x1b[1J" // Clear screen from the current cursor position to the beginning
<< "\x1b[H" // Move cursor to the coordinates 1,1
<< std::flush;
for (std::uint8_t i = 1; i <= uavcan::NodeID::Max; i++)
{
if (auto p = collector.getNodeInfo(i))
{
std::cout << "\033[32m---------- " << int(i) << " ----------\033[39m\n" // This line will be colored
<< *p << std::endl;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
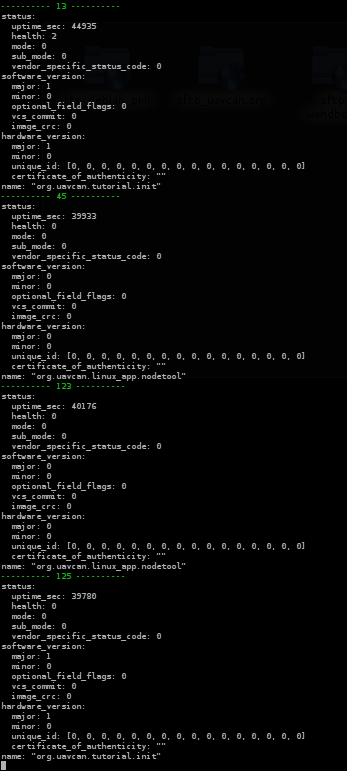
The output may look like this:
Running on Linux
Build the applications using the following CMake script:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)
project(tutorial_project)
find_library(UAVCAN_LIB uavcan REQUIRED)
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "-Wall -Wextra -pedantic -std=c++11")
# Make sure to provide correct path to 'platform_linux.cpp'! See earlier tutorials for more info.
add_executable(passive passive.cpp ${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/../2._Node_initialization_and_startup/platform_linux.cpp)
target_link_libraries(passive ${UAVCAN_LIB} rt)
add_executable(active active.cpp ${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/../2._Node_initialization_and_startup/platform_linux.cpp)
target_link_libraries(active ${UAVCAN_LIB} rt)