Application-level conventions
ID distribution
Message type ID
The valid range for message type ID is from 0 to 65535, inclusive (see CAN bus transport layer specification). The range is segmented as follows:
| ID range | Purpose |
|---|---|
| [0, 20000) | Standard message types |
| [20000, 21000) | Vendor-specific message types |
| [21000, 65536) | Reserved for future use |
Service type ID
The valid range for service type ID is from 0 to 255, inclusive (see CAN bus transport layer specification). The range is segmented as follows:
| ID range | Purpose |
|---|---|
| [0, 100) | Standard service types |
| [100, 200) | Reserved for future use |
| [200, 256) | Vendor-specific service types |
Node ID
The valid range for node ID is from 1 to 127, inclusive (see CAN bus transport layer specification).
The values 126 and 127 are reserved for debugging tools and should not be used for real nodes.
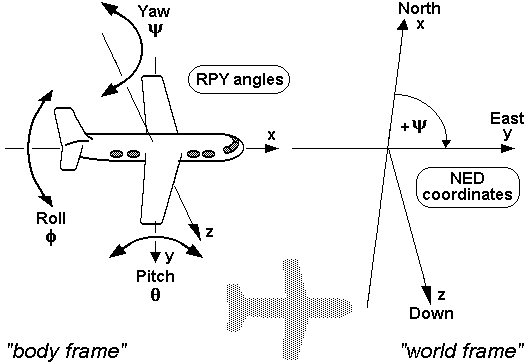
Coordinate frames and rotation representation
UAVCAN follows the conventions that are widely accepted in various aerospace applications.
All systems are right handed. In relation to a body, the standard is as follows:
- X forward
- Y right
- Z down
In the case of cameras, the following convention should be preferred:
- Z forward
- X right
- Y down
For world frames, the North-East-Down (NED) notation should be preferred.
The default rotation representation is quaternion. The coefficients are ordered as follows: X, Y, Z, W.
Angular velocities should be represented in fixed axis roll (about X), pitch (about Y), and yaw (about Z).
Matrix representation
Matrices should be represented as flat arrays in row-major order. There are some standard ways to represent an N-by-N square matrix in a one-dimensional array:
- An empty array represents a zero matrix.
- An array of one element represents a scalar matrix.
- An array of N elements represents a diagonal matrix, where each array member Ai equals the matrix element Mi,i.
- An array of ((1+N)*N)/2 elements represents a symmetric matrix, where array members represent elements of the upper-right triangle arranged in row-major order. For example, a 3-by-3 symmetric matrix can be represented as a flat array containing 6 matrix elements in the following order: [M1,1, M1,2, M1,3, M2,2, M2,3, M3,3].
- An array of size N2 elements represents a full square matrix.
Covariance matrix
A zero covariance matrix represents an unknown covariance.
Positive infinity in variance means that the associated value is undefined. Alternatively, in some cases, the value itself can be set to NAN (not-a-number float constant) to indicate that the parameter value is not defined. Note though that it is recommended to avoid NAN and infinities whenever possible for portability reasons.
Engineering units
All units are SI units, unless explicitly noted otherwise.
The following field naming convention is used:
- Fields that contain values not in SI units must be suffixed with the unit name, e.g.,
battery_capacity_wh(“wh” is for “Watt-hours” in this example). - Fields that contain values in SI units are not suffixed, e.g.,
voltage(implying that the units are Volts).
If an application designer chooses to deviate, such decision should be properly documented.